ONLINE APPOINTMENT
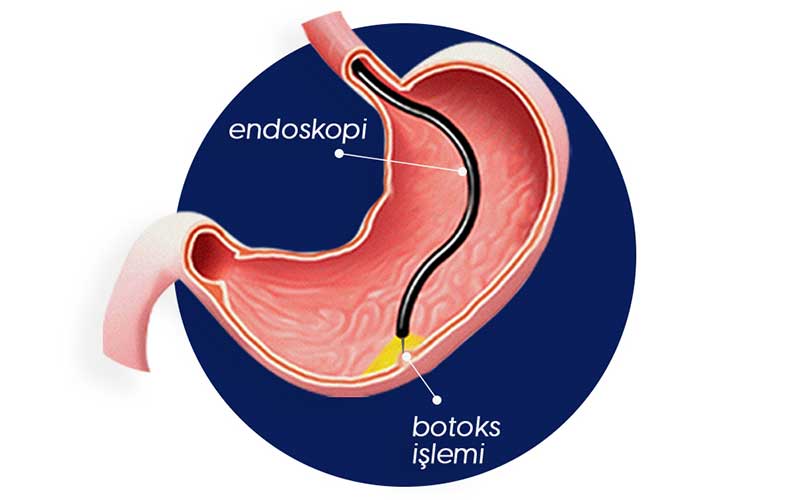
Gastric botox is a medical process using botulinum toxin injections to temporarily paralyze the stomach muscles and reduce the activity of the muscles in the stomach. This procedure is often applied to alleviate symptoms associated with some digestive system problems.
Stomach botox is widely used in the treatment of a condition known as gastroparesis. Gastroparesis is a condition where the rate of emptying slows down and means that food in the stomach cannot move properly. This
can happen when the stomach muscles do not work properly or the coordination between the esophagus and the intestines is impaired. Gastroparesis can cause mouth-taken food to remain in the stomach and digestive problems.
How Is The Gastric Botox Done?
Gastric botox is performed by making botulinum toxin injections into the stomach muscles. Botulinum toxin blocks the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine at the nerve endings, temporarily reducing the activity of the stomach muscles and slowing stomach movements. This can help keep food in the stomach longer and regulate the rate of stomach emptyness.
An Endoscopic Procedure
Stomach botox process is usually performed as an endoscopic procedure. The stomach is reached through an endoscope and botulinum toxin injections are made to the stomach wall. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia and the patient can be discharged on the same day.
Gastric botox can help alleviate the symptoms of gastroparesis, but its effects are temporary and may need to be repeated after a certain period of time. Also, gastric botox may not be suitable for everyone, and potential risks and benefits should be carefully evaluated. Therefore, it is important for patients considering gastric botox to meet with a gastroenterologist or digestive system specialist to assess their condition and determine appropriate treatment options.
Who is Stomach Botox Suitable for?
Gastric botox is a medical process that is usually done to treat stomach muscles and some stomach-related conditions. Therefore, gastric botox is not a suitable method for everyone and is recommended for candidates determined according to certain criteria.
It is important that individuals considering gastric botox are evaluated and guided by a gastroenterologist or digestive system specialist.
Gastroparesis – Those with Gastric Emptying Problems
Gastroparesis is a condition in which the rate of emptying slows down, and it can occur when the stomach muscles do not work properly or when the coordination between the esophagus and the intestines is impaired. To relieve the symptoms of gastroparesis, gastric botox can be considered.
Those with Stomach Ulcers
Due to stomach ulcers or some other stomach-related conditions, stomach muscles may become overactive. In
this case, gastric botox can be considered to relieve symptoms of stomach ulcers.
Cases where Other Treatment Methods Are Insufficient
If other treatment methods such as gastroparesis or stomach ulcers, diet and medication are not provided with adequate results, gastric botox may be considered.
Those With Surgical Risk
For patients who are not suitable for surgical treatment or have a high risk of surgery, gastric botox may be a less cut option.
However, stomach botox may not be suitable for everyone, and potential risks should also be considered. There may be risks such as infection, stomach damage or allergic reaction, especially during stomach botox procedure. Also, stomach botox effects are temporary and may need to be repeated after a certain period of time.
It is important for individuals considering gastric botox to consult with a gastroenterologist or digestive system specialist to assess their condition and choose the most appropriate treatment option. The specialist will decide whether the gastric botox process is appropriate, taking into account the patient’s health status.