Free Consultation Form
Hip Anatomy
The hip is a joint that connects the thigh bone to the pelvis. There is a ball-shaped tip at the top of the thigh and it sits in a slot. The hip is the body’s most flexible and most capabale joint that can move forward, backward, sideways.
On a healthy hip, a soft texture called cartilage wraps around the ball and slot to help them slide together comfortably. If this cartilage is eroded or damaged, the bones will rub against each other and harden. This condition, namely osteoarthritis, causes pain and restricts movement.
A hip with arthritis can make walking, or even sitting or getting up in a chair painful. If you have been diagnosed with hip arthritis, you may not need surgery. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or physical therapy can provide relief. But if these efforts do not relieve symptoms, they should consult an orthopedic surgeon.
Hip Replacement
Hip prostheses are artificial medical materials that are inserted instead of the hip part of the person that needs to be replaced. When other treatments do not help, a hip replacement is usually recommended if there is severe hip damage that interferes with a person’s life.
Hip prostheses can be manufactured as metal or plastic. The parts that need to be changed for hip replacement surgery are removed by separating from the joint. The prosthesis is placed in place of the removed part. There are different types of hip prosthesis, partial and whole.
Types Of Hip Replacement
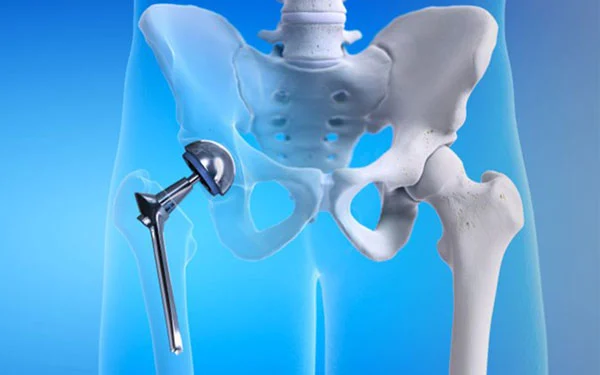
Whole Hip Replacement
Whole hip replacement is the most common hip surgery. This prosthesis uses a prosthesis to change the entire hip. During the procedure, surgeons place a trunk in the patient’s femur or thigh bone. They replace the head of the thigh bone with a ball and the natural nest in the hip joint with an artificial dish.
Partial Hip Replacement
A partial hip replacement removes and replaces the femoral head or thigh bone. A ceramic or metal ball is attached to the top of a body placed in the center of the femur. Surgeons typically perform this surgery to repair certain types of hip fractures.
Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery, also called hip arthroplasty, is the process of replacing damaged or worn parts of the hip joint with an artificial implant. If you have a hip fracture or have severe hip pain, hip replacement surgery may be recommended.
Diseases such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis are also among the reasons for experiencing these conditions. Hip replacement surgery can help improve range of motion, reduce pain, increase strength and improve quality of life.
What Diseases is Hip Replacement Surgery Used To Treat?
Hip replacement surgery is done if hip pain prevents you from doing daily tasks or walking independently. Not everyone with hip pain needs hip replacement surgery. Hip replacement can often help improve quality of life.
Hip replacement surgery is usually preferred as a result of damage to the hip joint and reduced mobility of the person. In addition, feeling pain in the hip area even during rest is a reason for surgery.
The most common cause of hip replacement surgery is calcification. Different conditions and life-long factors such as excessive wear and tear can affect the hip, causing increased pain and difficulty walking.
Conditions Where Hip Replacement Surgery is Required:
- Hip fracture
- Hip dislocation
- Osteoarthritis – calcification
- Pain in the front hips and groin
- Slipped femoral head pineal
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes
- Childhood hip disorders
- Persistent hip pain during rest
- Inflammatory arthritis: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis
- Restriction of physical activities due to hip pain
- Relief from pain is the biggest benefit and main cause of hip replacement surgery.
Hip Replacement Surgery Planning
Before hip replacement surgery, orthopedic surgery makes recommendations for prostheses according to the age of the person, activity level and quality of the bone. In order to prepare for surgery, the person undergoes various examinations. With these examinations, the medical risk of the person is evaluated before the operation.
- Physical examination
- Electrocardiogram
- Learning the Medical past
- Control of cardiovascular diseases
- Assessment of body weight
- Measuring the strength of the hip muscles with a muscle test

What Are The Methods of Hip Replacement Surgery?
Minimally invasive hip replacement surgery is a surgery used for any type of surgery that is less invasive than traditional or open surgery. Minimally invasive hip prostheses use fewer and smaller cuts around the hip joint.
The best candidates for minimally invasive hip replacements are typically people with minimal or moderate deformity. However, open surgery is preferred in cases where large parts of the hip need to be replaced. Open surgeries are standard types of surgery performed with wide incisions.
How is Hip Replacement Surgery Performed?
When total hip arthroplasty is planned, a surgeon replaces the required parts of the hip with a solid implant made of plastic and metal. The femoral head is also replaced during this surgery. Hip replacement can be performed under general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia.
Epidural anesthesia is a method of anesthesia in which the lower part of the body is numbed. This method can be used in people who do not need to be under general anesthesia. Surgeons use procedures that can be applied by making an incision from the back or front when performing hip replacement surgery. The operation usually takes about 60-90 minutes to complete.
What Should be Considered After Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Initiation of physical therapy
- Avoiding gaining too much weight
- Receiving therapeutic exercise support
- Use of toilet seat risers
- Keeping the wound area clean and dry
- Installing a handle for use in the bathroom
- Use of walking aids
- Physical activity under the supervision of a doctor
- Contact the doctor if necessary
- Using prescribed medications correctly
- Choosing shoes in a design that does not require long-term bending
After the operation, a dressing is applied that allows the hip to be held in place for 1 weeks. The stitches that close the cut are removed about 10-14 days after surgery and can be replaced with sterile strips. If your surgeon used glue to close the wound, the end stitches will gradually fall off after about 1 months.
Everyone recovers differently from hip replacement or revision surgery. The important thing is to keep moving, but to encourage yourself to accelerate and gradually become more active.
You may need to stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery. For the first 4 to 6 weeks after surgery, crutches may be needed to make walking easier and reduce pressure on the hip.
Most people are encouraged to walk with the help of a walking support immediately after surgery. Within an average of 2 to 3 months, the patient shows improvement that can continue with normal activities. However, it may take up to a year for the entire body to return to normal activity after the implant. For the first 3 months, the patient should avoid sitting, running, crouching and jumping in low chairs.
You may also need to start a doctor-controlled exercise program to get used to the hip implant. The surgeon informs the person about what activities he or she can do after the operation and prescribes medication for use after the surgery.
It usually takes at least 4-6 months for the patient to feel like they have returned to their pre-operative activity level. People with desk jobs may need to take at least 4 weeks off from work, and this period may be longer if complications arise.
What are the advantages of hip replacement surgery?
- Enhanced mobility
- Relieving pain due to hip damage
- Improved body and leg coordination
- Facilitate physical activities in everyday life